我的RDS实例存储空间占用不符合预期,如何排查RDS for MySQL 存储空间占用问题?
RDS for MySQL 的存储空间通常消耗在如下几个方面:
- MySQL 安装文件
- 用户创建的数据库
- 日志文件(general log & slow log & error log)
- 系统表空间
- 临时表空间
下面我们会从这几个方面进行排查:
分析数据库级别的空间占用
如下查询会显示出每个数据库占用的空间大小以及碎片大小:
SELECT
SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', 1 ) AS table_schema,
ROUND( SUM( its.allocated_size ) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2 ) "size in GB",
ROUND( SUM( t.data_free ) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2 ) "fragmented size in GB"
FROM
information_schema.innodb_sys_tables it
INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_sys_tablespaces its ON it.space = its.space
INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_sys_tablestats istat ON istat.table_id = it.table_id
INNER JOIN information_schema.TABLES t ON t.table_schema = SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', 1 )
AND t.table_name = SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', - 1 )
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC;
查看每个库中每个表的大小,可以找到占用空间最大的表:
SELECT
SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', 1 ) AS table_schema,
t.table_name,
ROUND( its.allocated_size / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2 ) "size in GB",
ROUND( t.data_free / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2 ) "fragmented
size in GB"
FROM
information_schema.innodb_sys_tables it
INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_sys_tablespaces its ON it.space = its.space
INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_sys_tablestats istat ON istat.table_id = it.table_id
INNER JOIN information_schema.TABLES t ON t.table_schema = SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', 1 )
AND t.table_name = SUBSTRING_INDEX( it.NAME, '/', - 1 )
WHERE
t.table_schema NOT IN ( 'performance_schema', 'mysql', 'information_schema' )
ORDER BY 4 DESC;
查询临时表/临时表空间占用大小
查看临时表空间占用大小:
SELECT file_name, tablespace_name, table_name, ENGINE, index_length
, total_extents, extent_size
FROM information_schema.files
WHERE file_name LIKE '%ibtmp%';
查看内部临时表占用大小:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.innodb_sys_tables
WHERE NAME LIKE '%#%';
查询共享表空间占用大小
SELECT file_name, tablespace_name, table_name, ENGINE, index_length
, total_extents, extent_size
FROM information_schema.files
WHERE file_name LIKE '%ibdata%';
同时,共享表空间一旦膨胀就无法缩小,不过您可以转储所有 InnoDB 表并将这些表导入到新的 MySQL 数据库实例中[3]。
查询日志占用大小
对于错误日志,慢日志,审计日志的大小,我们可以从RDS 控制台上查看到,选择您的实例,选择"实例信息","使用量统计部分,如下所示:
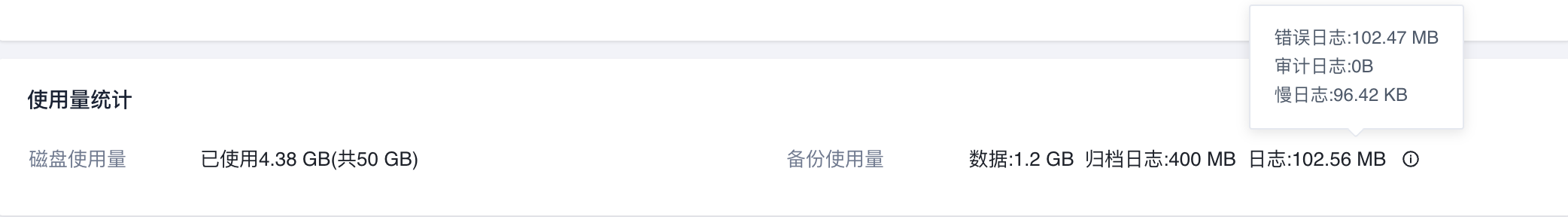
通过上述的分析,我们基本可以明确空间占用情况,下面是一些对应的解决方案,请您参考:
临时表空间占用过大
临时表空间过大通常来说意味着SQL可能不够优化,在运行过程中产生了大量的临时文件,您需要优化您的SQL语句来减少临时表空间的占用。
同时需要注意的是,在MySQL 5.7 版本中,SQL结束后,会标记删除,但是空间依然不会返还给操作系统,如果需要返还,则需要重启数据库[1], MySQL 官方文档中有如下描述:
To reclaim disk space occupied by a temporary tablespace data file, restart the MySQL server. Restarting the server removes and recreates the temporary tablespace data file according to the attributes defined by innodb_temp_data_file_path.
数据库中表碎片太多
您可以运行如下SQL语句来消除表空间碎片,需要注意的是,请您在业务低峰期进行此操作,避免对业务造成影响[2]。
mysql> ALTER TABLE <table_name> ENGINE=INNODB;
或者您可以运行如下语句:
mysql> OPTIMIZE TABLE <tablename>;
日志文件占用过大
如果是错误日志占用空间过大,我们可以查看日志中是否有持续的错误或者警告,然后进行具体的分析。
如果是慢日志占用空间过大,首先您可以检查慢日志相关的参数,long_query_time意味着SQL的实际执行时间超过多少秒会记录到慢日志中[4],log_queries_not_using_indexes 意味着需要记录所有未使用索引的语句[5],请检查这两个参数的设置是否符合您的预期:
mysql> show variables like 'long_query_time';
+-----------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+----------+
| long_query_time | 1.000000 |
+-----------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
mysql> show variables like 'log_queries_not_using_indexes';
+-------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------------------+-------+
| log_queries_not_using_indexes | OFF |
+-------------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
[1] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-temporary-tablespace.html
[2] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-file-defragmenting.html
[3] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-system-tablespace.html
[4] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-system-variables.html#sysvar_long_query_time
如果您有其他问题,欢迎您联系火山引擎技术支持服务

